1. The accuracy grades of linear guide rail are divided into (walking parallelism, taking the guide rail 100mm long as an example), general grade (unmarked /C)5μm, (H)3μm, precision grade (P)2μm, precision grade (SP)1.5μm and precision grade (UP)1μm according to the use of different machines. Preload the slider. Generally, preloading is divided into medium preloading and heavy preloading without preloading. The greater the preloading, the better the rigidity. Load: Generally, at the beginning of selection, it is concluded that 1/3 of rated dynamic load is the upper limit of practical load. Therefore, it is generally ensured that there is no sinking when it is added to medium preloading. If the guide rail is used up and down, it will play a guiding role. How much the slider rises is related to the screw or other transmission methods used, but not to the slide rail and slider.
2. There are basically three kinds of different brands. Usually, the gap effect of light preloading and medium preloading can affect the walking accuracy, load bearing ability and rigidity of the guide rail. And the guide rail with gap is selected, which can reduce the oscillation and impact caused by reciprocating motion to a certain extent.
3. When loading, the slider won’t sink much, so it should be called elastic deformation. If you want to say how much, no guide rail material is marked now, because it can be neglected.
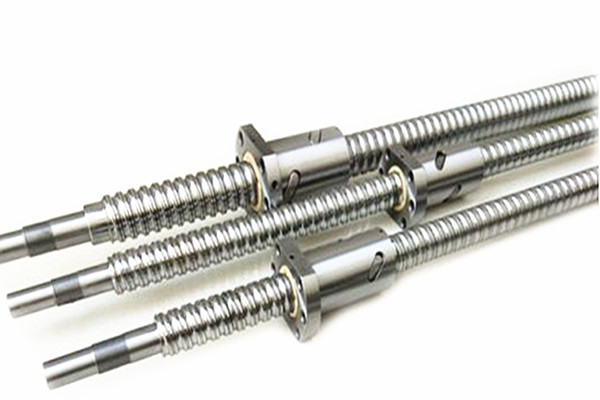
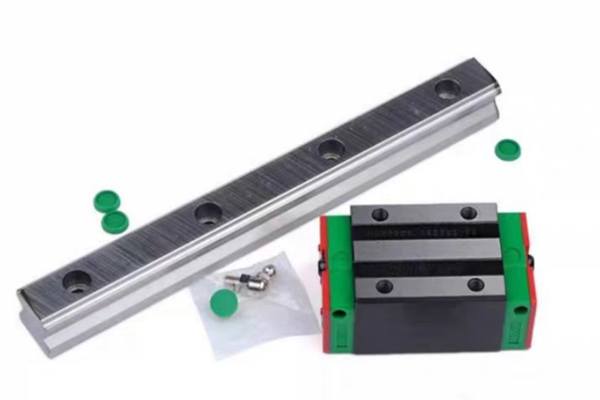
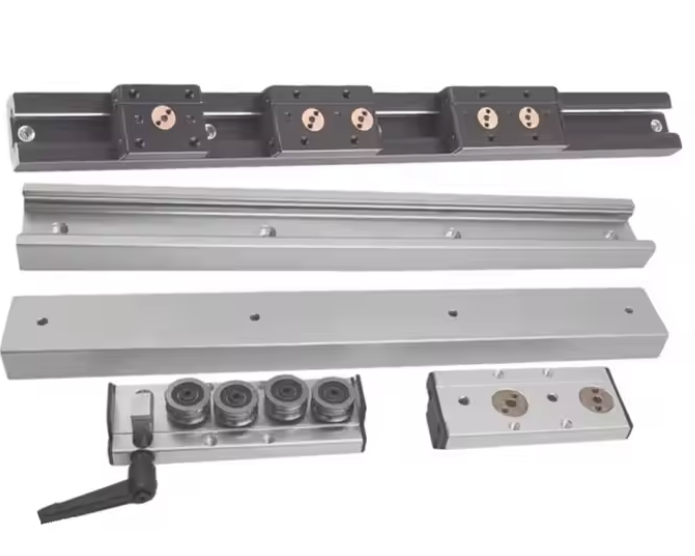
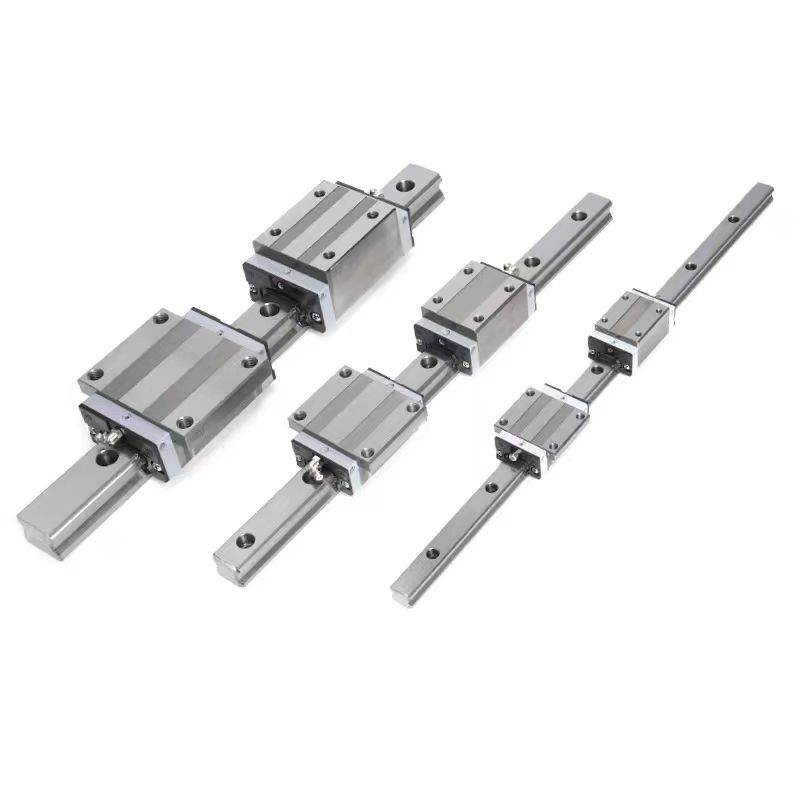
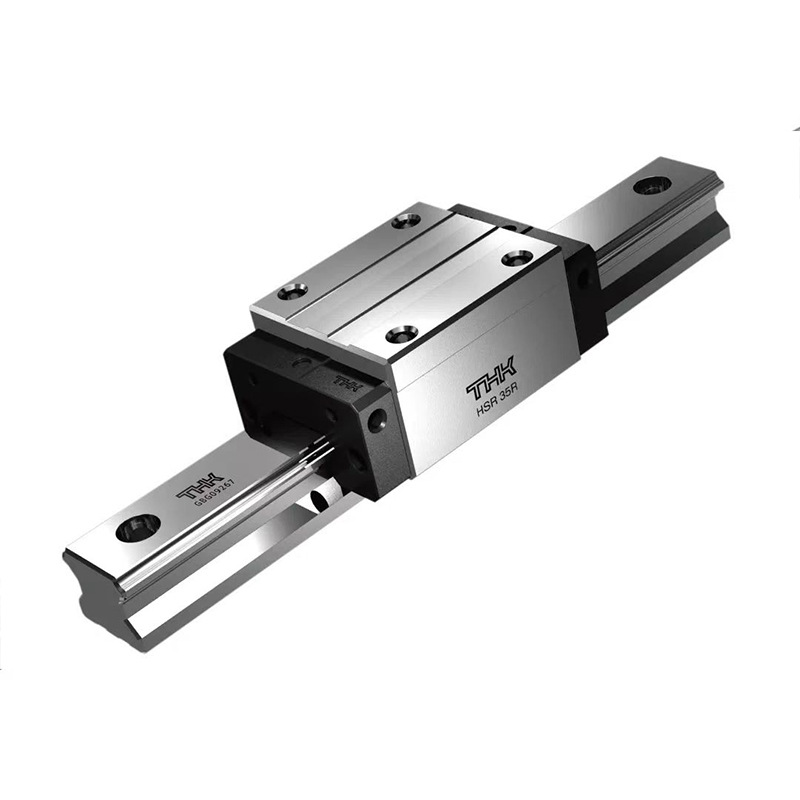
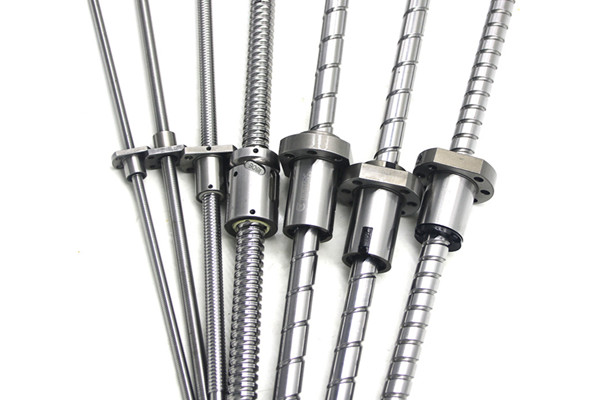
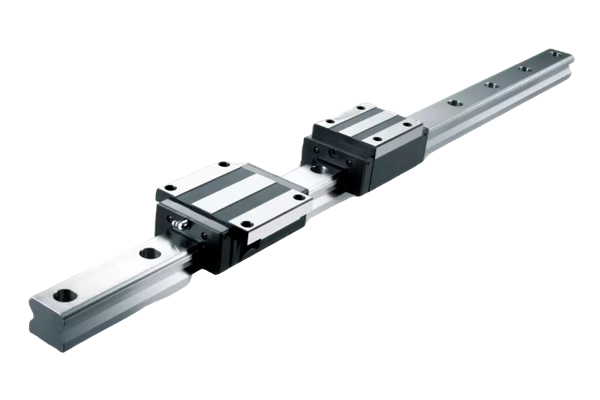






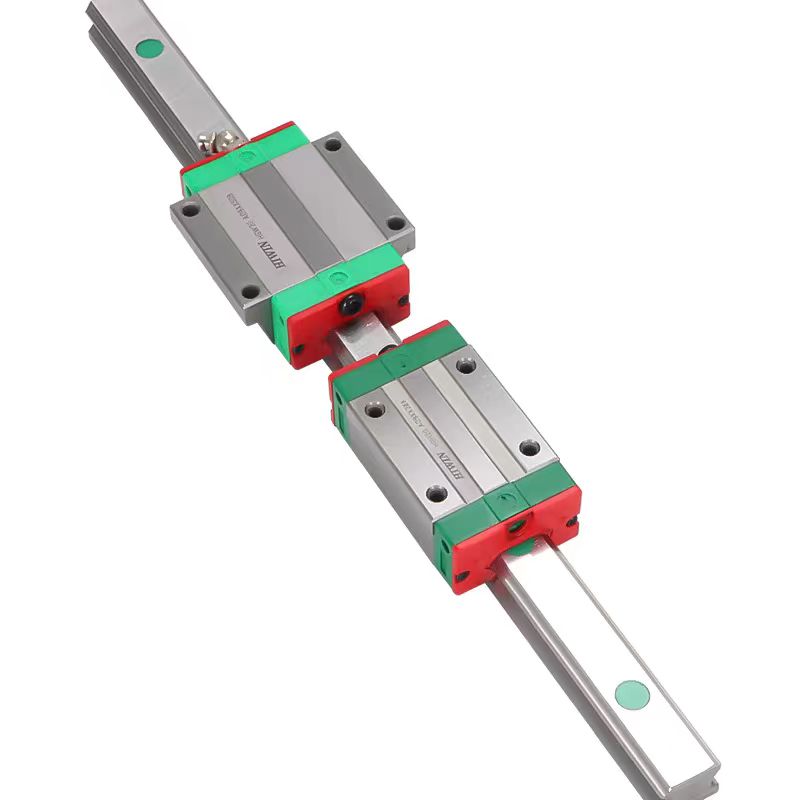

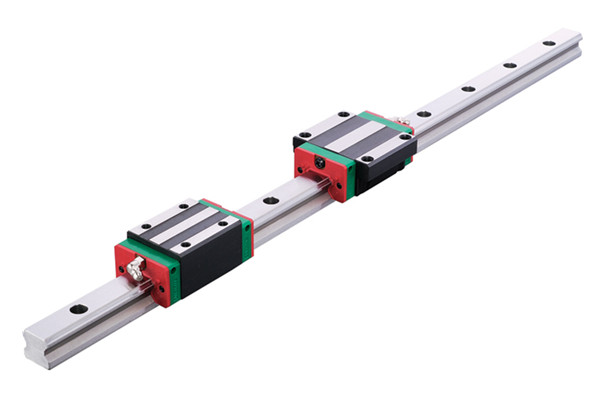




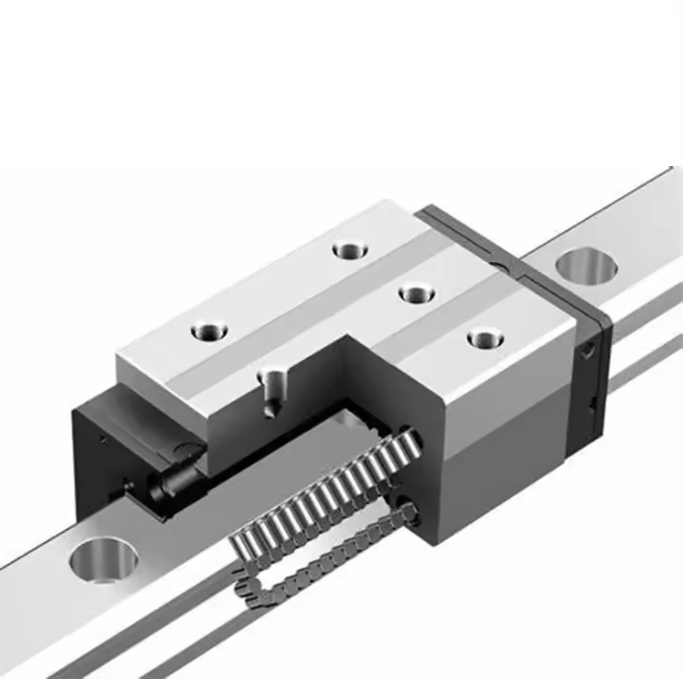


 Classification of Linear Guides
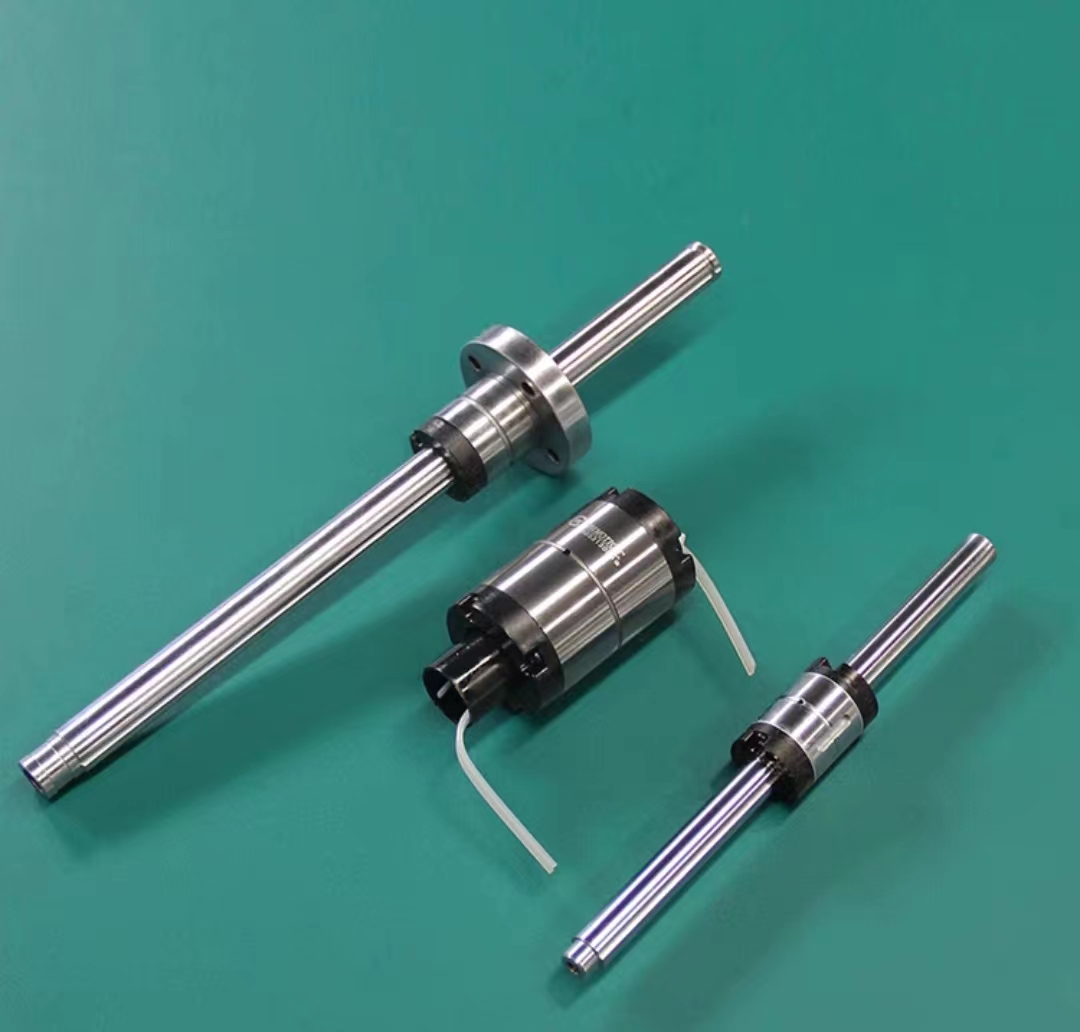
Classification of Linear Guides Reasons that affect the normal use of ball screws
Reasons that affect the normal use of ball screws