When to use ball screw, When to use trapezoidal screw?
How to select ball screw (or trapezoidal screw) and motor according to the requirements of precision, speed and load?
What are the common forms of supporting structures at both ends? (fixed-supported)
What is the structural design of nut decoupling at long stroke?
Let’s look at the difference between ball screw and trapezoidal screw with these questions, and explain it roughly from the following 10 aspects.
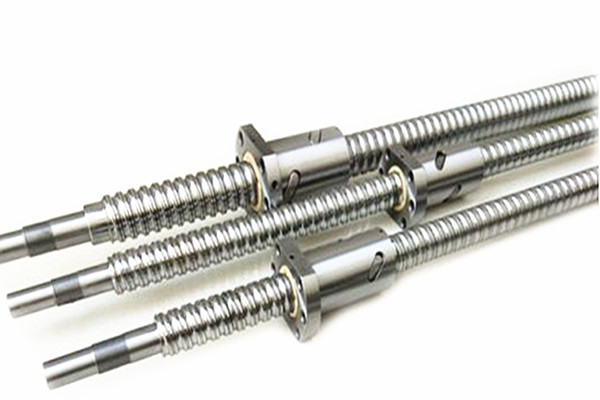
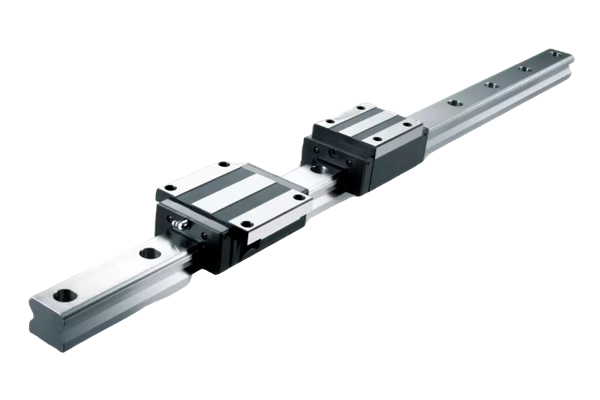
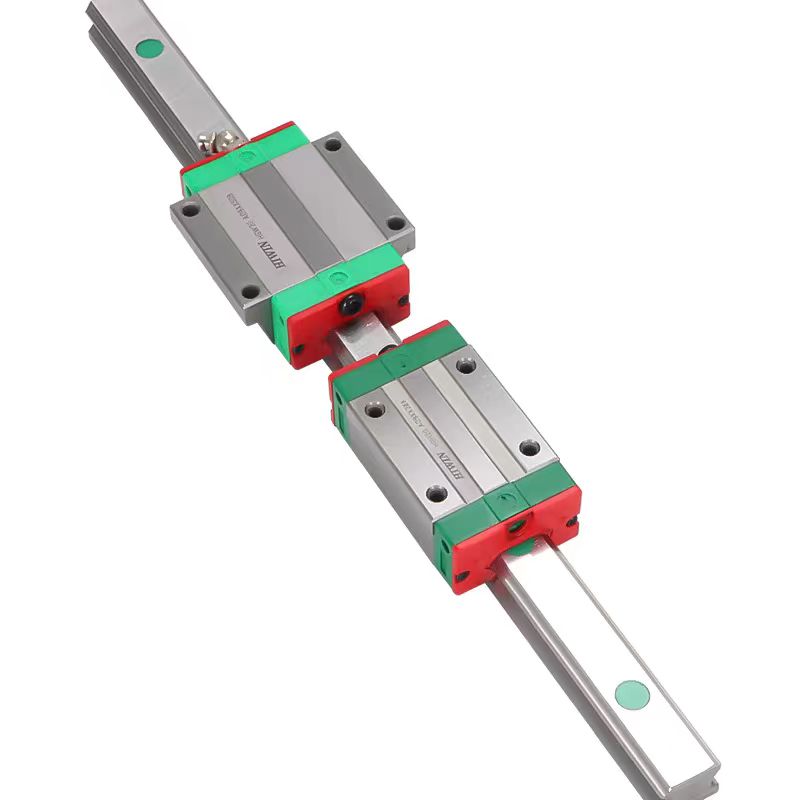
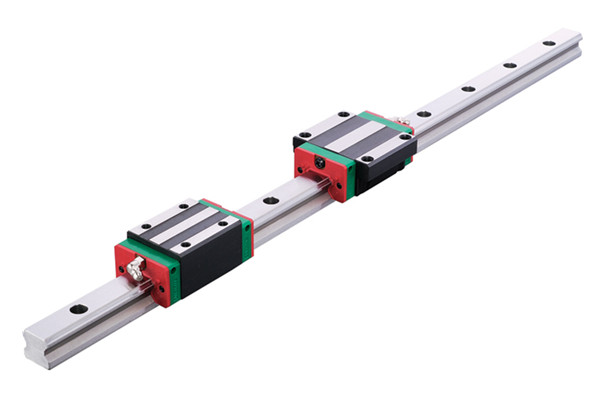
1. Different structures.
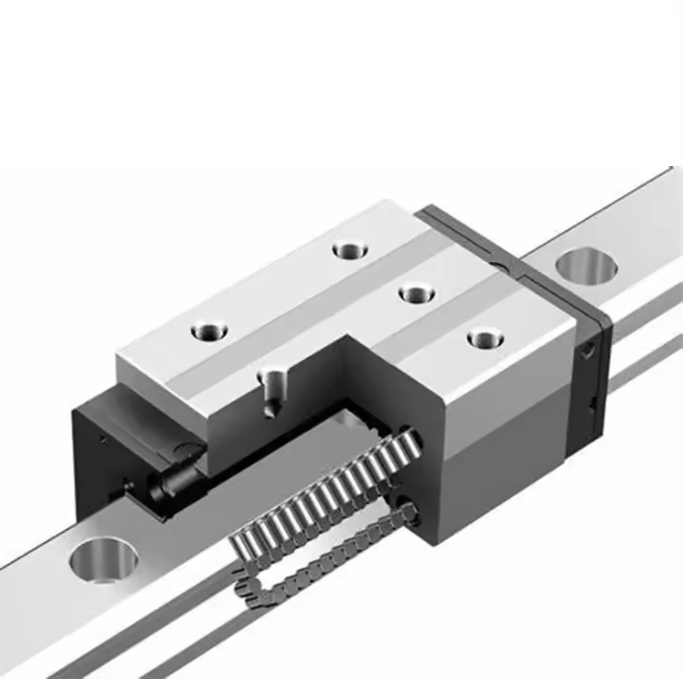
The movement principle of trapezoidal screw and ball screw is the same, but the difference is that there is no ball in trapezoidal screw, so the movement between nut and screw shaft depends entirely on mechanical contact to produce sliding, which is sliding friction, so trapezoidal screw is also called sliding screw.
Therefore, the structural difference between the two is summarized in one sentence: the ball screw is rolling friction and the trapezoidal screw is sliding friction.
2. Different transmission efficiency.
For example, NSK and THK show that the friction coefficient of ball screw is between 0.003 and 0.01, while that of trapezoidal screw is between 0.1 and 0.2.
For example, REXROTH shows that the friction coefficient of ball screw is between 0.005 and 0.01, while that of trapezoidal screw is between 0.2 and 0.3.
This is why the transmission efficiency of most ball screws is as high as 90%, and some even reach more than 95%, while the transmission efficiency of most trapezoidal screws is lower than 70%. trapezoidal screw is not suitable for high-speed operation, and its maximum speed is generally not more than 3000RPM. And the ball screw, because it is rolling friction, does not generate so much heat, and its speed can reach very high, such as 10000RPM. The efficiency of ball screw is 2-4 times that of trapezoidal screw, so generally speaking, when the same lead is used to drive the same load, ball screw has more advantages.
3. Different self-locking
Theory shows that when the transmission efficiency of screw is greater than 50%, there is no self-locking, and when the transmission efficiency is less than 35%, there is self-locking. Therefore, ball screw has no self-locking, while trapezoidal screw has certain self-locking.
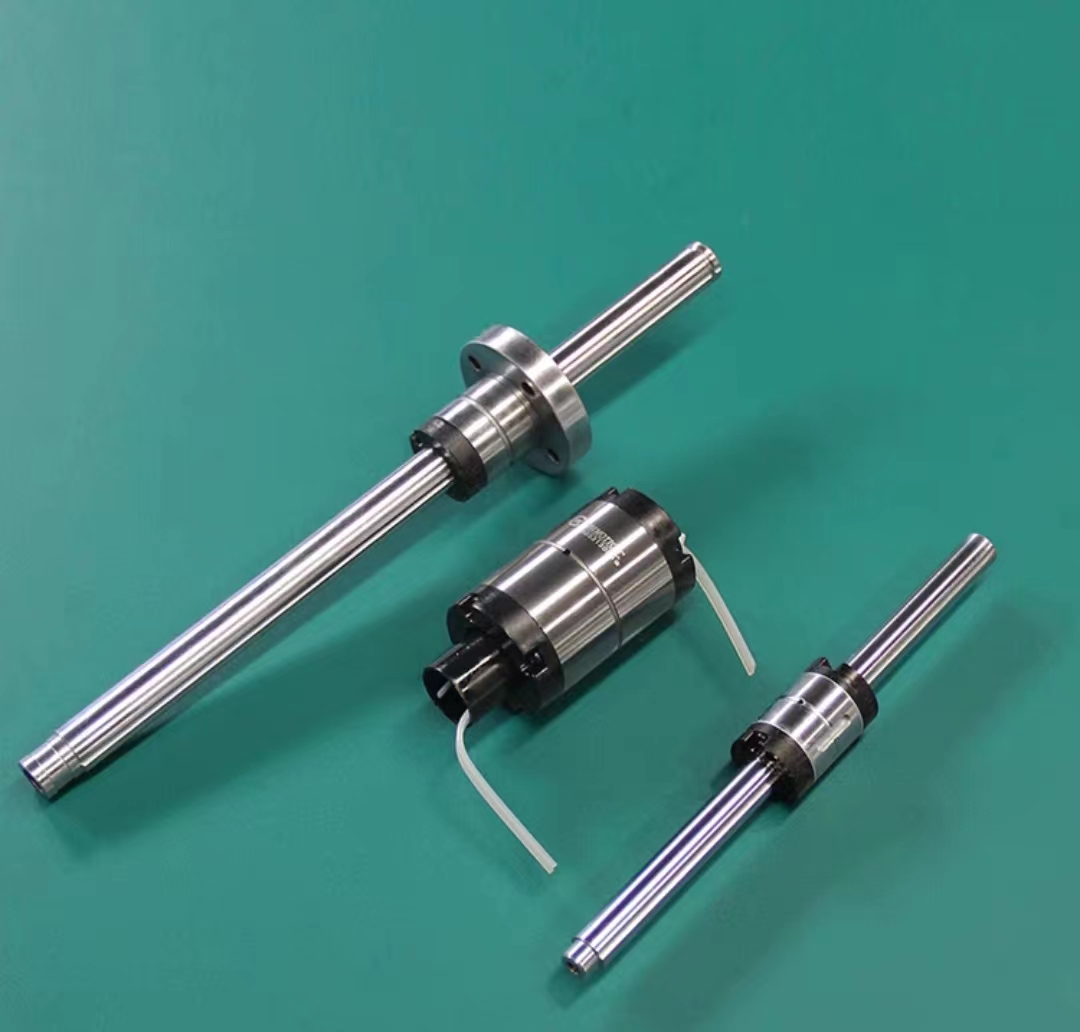
The trapezoidal screw shaft is also made of stainless steel or alloy steel. As for the nut, it is a little different from the ball screw. In many cases, the trapezoidal screw nut will use nonmetallic materials.
4. Different materials
The ball screw shaft is generally made of stainless steel or alloy steel, while the nut is generally made of copper, because copper can bear a large load and has a small friction coefficient, which has a certain self-lubricating effect. Just like some common linear bearing or plane skateboards, copper is also used, which is precisely the reason.
The trapezoidal screw shaft is also made of stainless steel or alloy steel. As for the nut, it is a little different from the ball screw. In many cases, the trapezoidal screw nut will use nonmetallic materials.
5. Different manufacturing methods and final precision
Generally, there are two processing methods for ball screws, one is grinding and the other is tying. The general precision of rolling ball screw is C7 C7(±50um/300mm), C8 C8(±100um/300mm) and C10 C10(±210um/300mm).C0-C5 belong to grinding grade screws, and the highest precision of grinding ball screws can reach C0 grade, that is, 3 um/100mm, and even ball screws with low grade C5 can achieve the precision of ±18um/100mm. Usually C5 and C3 (such as TBI and GTEN brands).
Trapezoidal screw has three manufacturing methods: rolling, cutting and grinding.
It is better than cutting, because rolling can get a harder surface with superior surface finish. However, as far as precision is concerned, grinding can obtain the highest precision, followed by cutting, and rolling can obtain the lowest precision.
For other differences, please see the next article.













 COUPLING
COUPLING Trapezoidal screw
Trapezoidal screw